Organic-inorganic nanocomposites as photonic recording media
Department of Electronics Engineering
Professor Yasuo Tomita
ytomita@ee.uec.ac.jp
http://talbot.ee.uec.ac.jp/
Professor Yasuo Tomita
ytomita@ee.uec.ac.jp
http://talbot.ee.uec.ac.jp/

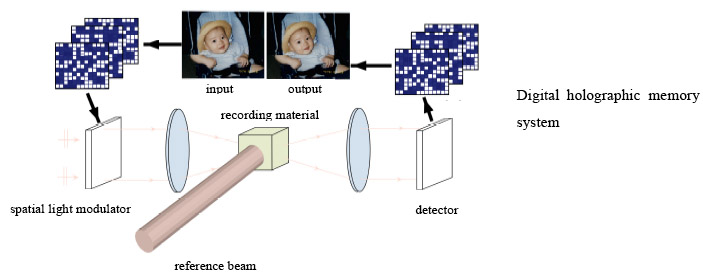
Methods being capable of recording temporal and/or spatial information embedded in coherent optical waves have received much attention owing to ever-increasing demands for more efficient and much denser information handling capabilities. Volume holographic memories (called holographic data storage systems: HDS) store optical wavefronts as 3D information in space and have been phenomenal in the last ten years owing to their ultrahigh storage capacity and ultrafast access speed with parallel recording/readout.
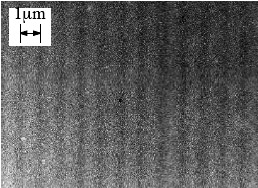
distribution of SiO2 nanoparticles
To realize HDS, we need photonic recording media possessing high recording sensitivity and dynamic range (high-contrast refractive index changes). To meet these requirements, we have developed novel organic-inorganic nanocomposite photopolymers being capable of permanent volume holographic storage with high diffraction efficiency and high dimensional stability. This photopolymer system also opens a possibility of creating completely new photonic materials such as linear and nonlinear photonic crystals.