Device Applications of Silicon-Related Nanoparticles
Department of Electronic Engineering
Department of Communications and Systems Engineering
Professor Shinji NOZAKI
nozaki@ee.uec.ac.jp
http://nano.ee.uec.ac.jp

Silicon-related nanoparticles refer to silicon (Si) nanocrystals surrounded by SiO2 or Si3N4, as shown right. Here, the Si nanocrystals are crystalline Si particles with a size in the order of 10-9 m. The Si nanocrystals in the Si-related nanoparticles are ideal quantum dots with a stable surface, where carriers (electrons and holes) and phonons are to be confined.
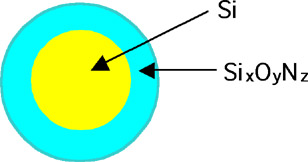
Silicon-Related Nanoparticle
The physical properties unique to silicon quantum dots make Si more attractive as a material of optoelectronic and functional devices. The sizes of Si quantum dots can be precisely controlled by their interaction with coherent light causing so-called photo-oxidation.
The average size of the Si nanocrystals is determined to be 2 nm from the phonon confinement in the Raman spectrum. A good-quality of SiOx film was obtained by evaporating the Si-related nanoparticles in vacuum and photo-oxidizing the deposited film. In the right figure showing the peak wave numbers in Fourier Transform of Infrared Absorption (FTIR) spectra of various silicon oxides, x in SiOx obtained from the Si-related nanoparticles is close to 2, suggesting oxide with a quality as good as thermal oxide's. This achievement is to be well appreciated in the Si VLSI and other device technologies, because it realizes low-temperature deposition of high-quality oxide, which could not be achieved by evaporation of the conventional SiO powders.
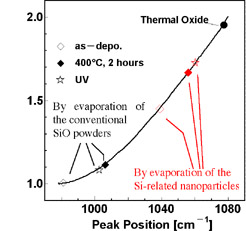
Oxide Quality by FTIR